Accreditation
National: UNGGUL (EXCELLENT)
International: AUN-QA, FIBAA

Intake Period
Annually
Duration
8 semesters (144 credits)
Courses
Fulltime
Lectures
On campus
Admission Informations: PPMB UNAIR Website
- Profile
- Courses
- Learning Outcomes
- Course Schedule
- Academic Status
- Student Organizations
- Scholarships
- Alumni
- Research
| RESEARCH |
Research and community outreach are organized by Faculty of Psychology and are arranged in a research roadmap by each department.
Information about research and community service interest can be located in the profile of each lecturer on this link: Lecturers Profile & Expertise.
Data about researches conducted by lecturers can be located on this link: Research
| COURSES |
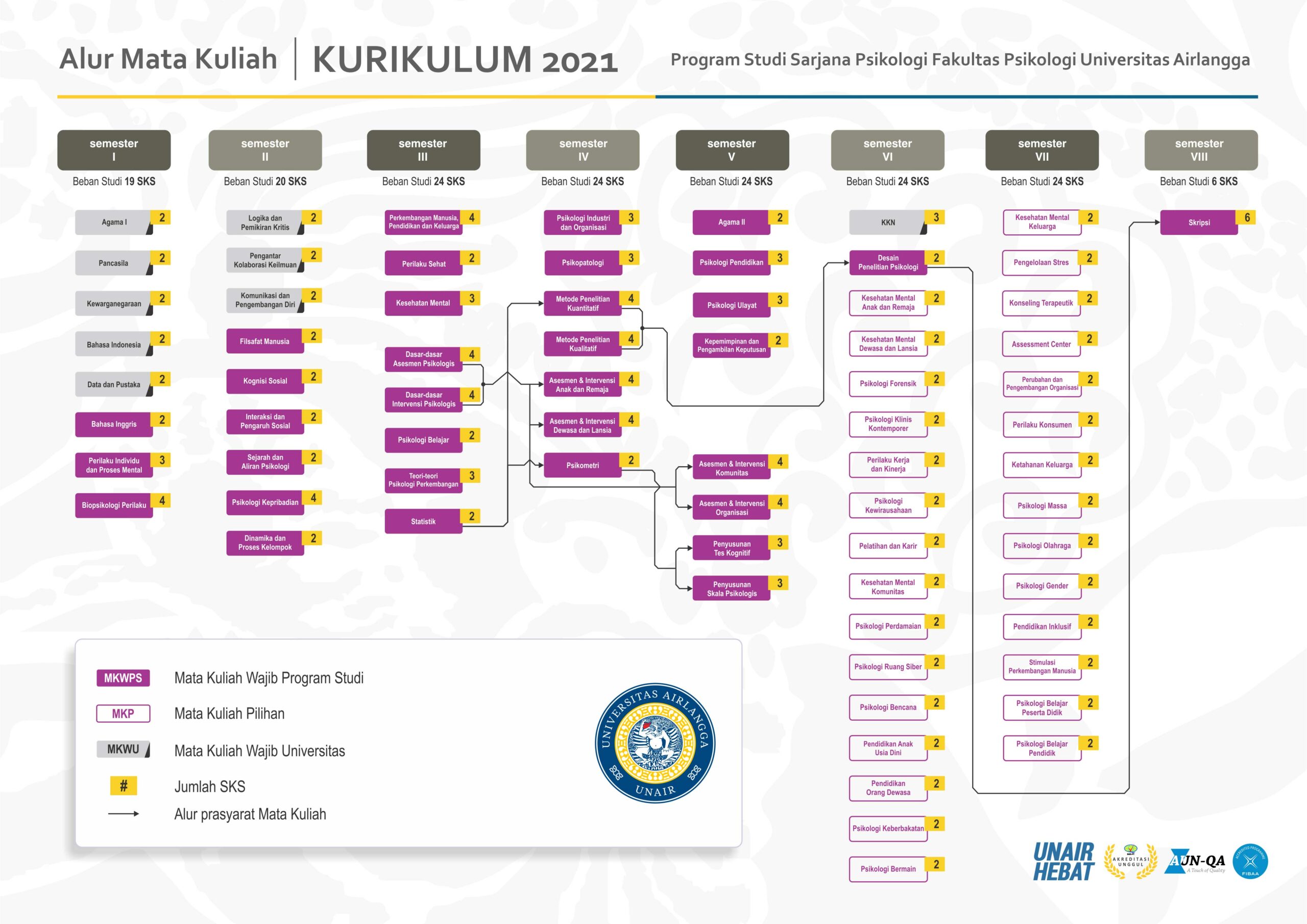
Buku Panduan Akademik Sarjana Psikologi UNAIR Kurikulum 2021 (PDF)
INTERNATIONAL CLASS
- Academic Mobility Exchange for Undergraduate at Airlangga (AMERTA). Bachelor of Psychology Programme offers some courses for international class centrally managed by Universitas Airlangga.
- Inbound-outbond student mobility UNAIR-UUM. Bachelor of Psychology programme and School of Applied Psychology, Social Work, and Policy, Universiti Utara (Malaysia) organizes student exchange from both programme, where students from each one will study for one semester in the partner-institution with a credit transfer system.
- 2+2 Articulation Program (collaboration with QUT, Australia). This programme is a collaboration between Bachelor of Psychology programme with School of Psychology and Counselling, Queensland University of Technology (Australia) which offers double degree. Students will spend their first two years in UNAIR and the next two years in QUT.
| LEARNING OUTCOMES |
Currently, there are two curricula that apply in Bachelor of Psychology programme, namely curriculum of 2009 and curriculum 2014. Curriculum of 2009 applies for students of Class 2012 and earlier. Meanwhile, curriculum of 2014 is the redesign of the curriculum of 2009 which applies for students of Class 2013 and later.
Learning Outcomes in Curriculum of 2009
| Area of Competence | Learning Outcomes |
| Personal: ability to develop self-awareness and characters building. | 1. Able to apply psychology-specific content and skills, effective self-reflection, project-management skills, teamwork skills, communication skills, and career preparation inline to contextual values and professional standard. |
| Conceptual: ability to mastery psychological concepts and theories | 2. Able to demonstrate fundamental knowledge and comprehension of the major concepts, theoretical perspectives, historical trends, and empirical findings to discuss how psychological principles apply to behavioural problems. |
| Research and assessment: ability and skills to conduct research and assessment about psychological issues of individual and community. | 3. Able to demonstrate competence in theory use as well as designing and executing research and assessment plans. |
| Creation and intervention: ability to create programmer or products to promote individual and community well-being | 4. Able to design innovative programmes or products to optimize contributions to society’s wellbeing. |
Learning Outcomes in Curriculum of 2014
MAIN COMPETENCIES
| No | Learning Outcomes | Courses |
| 1 | Showing behaviour based on noble values, respecting differences, and empathetic. |
|
| 2 | Mastering major theoretical concepts of human mental functions and processes (e.g. memory, emotion, and motivation), as well as history and schools of psychology. |
|
| 3 | Mastering the theoretical concepts of the influence of brain and nervous system on behaviour. |
|
| 4 | Mastering the theoretical concepts of learning process. |
|
| 5 | Mastering the theories of personality |
|
| Mastering the theoretical concepts of human developments from conception stage until elder stage. |
|
|
| 7 | Mastering the theoretical concepts of mental health and psychopathology. |
|
| Mastering the principles of community approach in seeking mental health improvement. | ||
| 8 | Mastering the theoretical concepts of human relationships with their social environment. |
|
| 9 | Mastering the concepts and basic theories of Industrial and Organisational Psychology. |
|
| 10 | Mastering basic statistical techniques and basic research methodology. |
|
| 11 | Mastering phases of preparing psychological scale, concepts in psychological measurement (validity, reliability, norms), classical test theory, and basic concepts in psychometric. |
|
| 12 | Able to develop psychological measurement instrument based on the rules of classical test theory | |
| 13 | Mastering basic concepts and principles of psychodiagnostic, interview techniques, observation techniques, and theoretical concepts that underlie the psychological tests. |
|
| 14 | Understanding basic methods of counselling, psychoeducation, training and psychotherapy. |
|
| 15 | Understanding theoretical concept of interpersonal communication and mass communication. |
|
| 16 | Having an ability to explain the ideas by writing, showing presentation effectively, and using information technology with responsible. | |
| 17 | Understanding scientific writing methods based on American Psychological Association (APA). | |
| 18 | Understanding Ethics Principles of Profession and Ethic Codes of Psychology in Indonesia. |
|
| 19 | Responsible on work result based on Ethic Codes of Psychology in Indonesia. | |
| 20 | Mastering theoretical concept about self-development and carrier. |
|
| 21 | Capable on doing rapport and develop effective professional relation, and develop a healthy interpersonal relation. |
|
| 22 | Mastering on doing interview, observation, psychological test based on psychodiagnostical principle and Ethic Codes of Psychology in Indonesia. | |
| 23 | Able to analyse non-clinical psychological problems and behavioral problems and provide alternative solutions among existed solutions. | |
| 24 | Capable on doing psychological intervention by using counselling method, psychoeducation, training and other intervention techniques based on theoretical concept of psychology and ethic codes of psychology in Indonesia. | |
| 25 | Understanding on doing psychological research by using quantitative research method (at least descriptive statistical analysis or inferential bivariate, and non-parametric to observed variable) and by using qualitative research methods. |
|
| 26 | Able to plan and develop career and personal development |
|
SUPPORTING COMPETENCIES
| No | Learning Outcomes | Courses |
| 27 | Ability to explain basic concepts of science philosophy, such as paradigm, falsification, realism, and hypothetico-deductive model. |
|
| 28 | Ability to explain critically and argumentatively about philosophical problems of human nature associated with physical, metaphysical, and social features. |
|
| 29 | Ability to explain the impacts of science development and technology on global environment. |
|
| 30 | Creating a map/dynamic of developmental and educational issues at each stage of development using a family perspective. |
|
| 31 | Creating a scheme/diagrams of group influences dynamics on social institutions, as well as how groups teach individuals about what is appropriate and inappropriate, facilitate and impede change, mark levels of status, social class and power, and demonstrate prejudice and discrimination. |
|
| 32 | Mastering theoretical concepts and approaches of indigenous on individual and group behaviour. |
|
| 33 | Creating a scheme/diagrams of the dynamics of Indonesian current society behaviour using anthropology-psychological perspective. |
|
| 34 | Ability to apply Bahasa language in communicating, both orally and in writing based on applicable rules. |
|
| 35 | Ability to apply English language in communicating, both orally and in writing based on applicable rules. |
|
| 36 | Mastering theoretical concepts of family dynamics and development in relation to individual development. |
|
| 37 | Ability to design a community health promotion through intervention mapping approach. |
|
| 38 | Ability to recognize and develop potential leadership skills beneath themselves. |
|
| 39 | Ability to make a decision based on decisional making analysis techniques. | |
| 40 | Creating undergraduate thesis proposal based on topics and themes from each areas of interest. |
|
OTHER (SPECIFIED) COMPETENCIES
| No | Learning Outcomes | Course |
| 41 | Compiling lesson planning or managing early childhood education based on concept of child development (Developmentally Appropriate Practice/DAP) |
|
| 42 | Capable to design planning of learning programs for adults |
|
| 43 | Implementing programs for gifted individuals’ development on socio-emotional aspects, creativity, learning independence and career |
|
| 44 | Capable to make educational game tool (APE) as stimulation of development and learning media in education |
|
| 45 | Designing programs for preventing emotional and behavioral disorders in children and adolescents considering to the bio-psycho-socio-cultural and gender aspects |
|
| 46 | Capable to develop learning strategies for Special Needs Students in accordance with their specificity in Inclusion School |
|
| 47 | Make the right recommendations to help optimize progress and resolve individual issues at every stage of developmental age (child, adolescent, adult and elderly) |
|
| 48 | Create design planning community profiling activities for mental health improvement |
|
| 49 | Intervening addictions behaviour which emerged by the use of computer-mediated communication behaviour, both in individual and social terms. |
|
| 50 | Create design of conflict resolution within the context of Indonesian society |
|
| 51 | Capable to perform psychological handling of disaster victims based on Psychological First Aids approach and procedure |
|
| 52 | Capable to intervene to strengthen psychosocial capacity for communities in disaster prone areas (disaster mitigation) | |
| 53 | Identify risk factors that contribute to health problems by exploring determinant factors based on ecological approaches using intervention mapping measures |
|
| 54 | Performing assistance or psycho education for society related to human trafficking case |
|
| 55 | Designing a mass behaviour model for constructive interest in the life of society |
|
| 56 | Designing intervention models which able to increase positive work behaviour and reduce negative work behaviour |
|
| 57 | Arranging a business plan and conducting a research market related to business which they will do |
|
| 58 | Able to design a coaching for individual development in workplace |
|
| 59 | Designing a training which able to improve group effectivity for increasing mental health in organization |
|
| 60 | Designing module of organization culture change initiation |
|
| 61 | Creating a stress management project which related to personal stress cases in daily life |
|
| 62 | Able to perform psychological mapping of the perpetrators of criminal / criminal acts (criminal profiling) |
|
| 63 | Able to perform psychological autopsy of the crime victim | |
| 64 | Able to perform group counselling in case of substance abuse or risky behaviour of adolescence |
|
| 65 | Performing counselling for non-clinical problem in marriage and family |
|
| 66 | Designing preventive, promotive, and curative program towards psychological disorders in adult and elderly |
|
| COURSE SCHEDULE |
Learning activities are divided into two semesters in one year. The odd semester is held during August – January, while even semester is during February – July. The minimum number of meetings in one semester is 14 which can be conducted in various learning strategies, such as lecture, seminar, group discussion, field trip, research, and so on. Student can access their schedule through their respective account on Universitas Airlangga Cyber Campus (UACC).
| ACADEMIC STATUS |
Bachelor of Psychology programme is accreited ‘A’ based on Decision Letter No. 1386/BAN-PT/Akred/S/VII/2016, dated 29 July 2019, valid until 29 July 2021. Graduates will hold a Sarjana Psikologi degree (S.Psi, equivalent to Bachelor of Psychology). Students of 2+2 Articulation Program will hold Sarjana Psikologi degree and Bachelor of Behavioral Science degree.
| STUDENT ORGANIZATIONS |
Bachelor of Psychology programme offers opportunity for students to develop their soft skills and leadership potential through various student organization (Organisasi Kemahasiswaan - Ormawa): Student Executive Board (Badan Eksekutif Mahasiswa - BEM), Students Legislative Board (Badan Legislatif Mahasiswa - BLM), and Semi-Autonomous Board (Badan Semi Otonom - BSO). Activities of these student organisations are managed by the member, monitored by supervising lecturer, and reported periodically to the dean of the faculty.
| BEASISWA |
A number of scholarships is offered to the students and some of it are centrally managed by Universitas Airlangga. Scholarships are given to students who qualify for the requirements. The scholarships managed by UNAIR are:
- Beasiswa Masuk Universitas (BMU),
- BUMN Peduli Pendidikan,
- Bidik Misi,
- Peningkatan Prestasi Akademik (PPA),
- Bantuan Belajar Mahasiswa (BBM),
- Peningkatan Prestasi Ekstrakurikuler (PPE),
- Djarum Bakti Pendidikan,
- Bank Mayapada,
- Bank Eka Cipta,
- Semen Gresik,
- Indocement Tunggal Prakarsa,
- Pertamina Yekape,
- Supersemar,
- Bakti BCA
- Damandiri,
- Bank Indonesia,
- Bank Rakyat Indonesia,
- PT. Gas Negara,
- Marga Jaya,
- Indocement, etc.
| ALUMNI |
About APSILANGGA
Faculty of Psychology Universitas Airlangga has an alumni associate called APSILANGGA (Alumni Psikologi Universitas Airlangga / Associate of Psychology Universitas Airlangga Alumni). Various activities are organized by APSILANGGA, both by the steering committee and the alumni. Alumni of Faculty of Psychology Universitas Airlangga are actively involved in numbers of activities organized by the university, particularly those which are organized by IKA UA and Faculty of Psychology. APSILANGGA has officially served as a communication medium for alumni since 2003 through an Alumni National Discussion (Mukernas Alumni) in Surabaya Hilton Hotel. It was named IKA-PSIKOLOGI UNAIR then. In Mukernas III 2008, this organisation changed its name into APSILANGGA. In addition to its function as a communication portal, in its development, APSILANGGA has succeeded in becoming a place for self-development for alumni, students, and wider community. APSILANGGA organizes numbers of seminar and training program and shares information about job vacancy via alumni blog and official website of the faculty. It is deemed as an effective way for academic and non-academic improvement for alumni, students, and the community. Recently, APSILANGGA collaborated with HIMPSI Jatim (East-Java regional HIMPSI) to become a bridge for psychodiagnostic skill and professional knowledge improvement for alumni, students, and wider community. APSILANGGA also builds a social network to sharpen community’s or particularly alumni’s social concern by raising funds and providing financial aids for those in need.
APSILANGGA's Activities
Since 2000, APSILANGGA has created a milist (mailing list) as a communication medium for alumni (https://groups.yahoo.com/group/alumni_psi_unair). APSILANGGA also has a blog for alumni to share new information pertaining to work and carrier which is also integrated to the faculty website (https://www.psikologi.unair.ac.id/alumni). This blog serves as a portal for socialisation of alumni’s activity, information about alumni, work vacancy information, training and seminar information both by APSILANGGA or other organizers, profile of alumni’s achievement, and also information about faculty’s events, especially those involving alumni.
Some regular activities held by APSILANGGA are:
- Conference
- Seminar and training
- Reunion and Family Gathering
- Shared learning with students
- Other academic and non-academic activities.
| RESEARCH |
Research and community outreach are organized by Faculty of Psychology and are arranged in a research roadmap by each department.
Information about research and community service interest can be located in the profile of each lecturer on this link: Profil Dosen & Kepakaran.
Data about researches conducted by lecturers can be located on this link: Research
